Projects
Current Projects
Conversational XAI
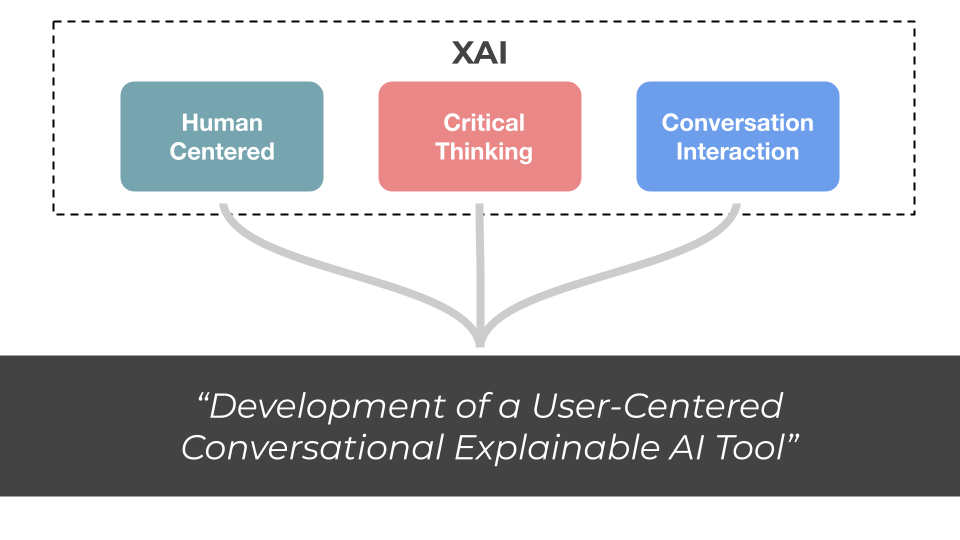
Conversational XAI is the theme of my PhD research project. Here's a brief summary. The general objective of research on XAI is to develop methods that can explain a decision made by a Machine Learning model. However, these methods are not accessible, since they often require programming knowledge and ML expertise. A recent effort to address this challenge is to employ an interdisciplinary approach using Human-Computer Interaction. Conversational XAI methods aim to provide a more familiar way of interacting with models by implementing an interface based on natural language. My PhD research goal is to bridge the gap between non-expert users and XAI techniques by developing a conversational tool leveraging user-centered approaches and natural language interaction.
Supervisors: Franco Raimondi and Fosca Giannotti.
Formerly: Pierluigi Crescenzi.
Interpretability of DRL agents
One of my research interests is applying Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) methods to autonomous agents. In particular, for agents developed using Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). This research branch started with a work in 2020 by investigating how the agents would perform in the same scenario but with different textures3. Then, a more rigorous assessment of how specific game object appearance affects an agent's performance2 followed. Explainable Reinforcement Learning (XRL) was also the subject of Alexandre Magno Master's research1.
Related publications
- Unveiling the Key Features Influencing Game Agents with Different Levels of Robustness
- Assessing the Robustness of Deep Q-Network Agents to Changes on Game Object Textures
- Investigating Deep Q-Network Agent Sensibility to Texture Changes on FPS Games
Past Projects
WorldDynamics.jl
WorldDynamics.jl is an open-source framework for world dynamics modeling and simulation. This project aims to provide a modern framework to investigate integrated assessment models of sustainable development, based on current software engineering and scientific machine learning techniques. Envisioned by Pierluigi Crescenzi and Emanuele Natale, WorldDynamics.jl is a Julia library to allow scientists to use and adapt different world models easily. By enabling an open, interdisciplinary, and consistent comparative approach to scientific model development, the goal is to inform global policy makers on environmental and economic issues.
Current Status: WorldDynamics.jl is being maintained by Aurora Rossi and Emanuele Natale.
Repository: WorldDynamics.jl GitHub
Documentation: WorldDynamics.jl Docs
Related publications
- WorldDynamics.jl: A Julia Package for Developing and Simulating Integrated Assessment Models
- Un framework open-source écrit en Julia pour la modélisation d’évaluation globale intégrée
Foraging Behavior
Although not a project itself, I have been using foraging environments as an evaluation testbed for Reinforcement Learning agents. I have used a foraging scenario in a Doom game in one of my first published papers4. Anderson Oliveira also used a foraging task in a 3D environment to evaluate the performance of different RL algorithms3. More recently, I was invited to give a talk at the Future of Foraging series2. Rômulo Férrer Filho developed a Curriculum Learning strategy to train foraging agents with both visual and auditory capabilities in his Master's research1.
Related publications
- Using Curriculum to Train Multisensory Foraging DRL Agents
- Deep Reinforcement Learning in Foraging Simulation
- Autonomous Foraging with SARSA-based Deep Reinforcement Learning
- On the Development of an Autonomous Agent for a 3D First-Person Shooter Game Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
DRLeague
DRLeague is a novel DRL environment, proposed to be open-source, and easily customizable, which supports mechanics for 3D games inspired by the popular “car football” game Rocket League. Besides the typical gameplay, there are four minigames based on the game mechanics with advanced physics simulation and fine-grained car control: penalty shoot, multiplayer penalty shoot, barrier kick, and aerial shoot. DRLeague started as a work for the Bachelor's thesis of Hyuan Farrapo. Then, the work was extended to the current environment version.
Repository: DRLeague GitHub
Publication: DRLeague: a Novel 3D Environment for Training Reinforcement Learning Agents
GymHero
Gym Hero is a Reinforcement Learning environment based on the game Guitar Hero. It consists of a similar game implementation, developed using PyGame, with four difficulty levels, and able to randomly generate tracks. On top of the game, a Gym environment was implemented to allow training and evaluation of Reinforcement Learning agents. GymHero was primarily the effort of Rômulo Férrer Filho in his Bachelor's thesis.
Repository: GymHero GitHub
Publication: Gym Hero: A Research Environment for Reinforcement Learning Agents in Rhythm Games
